- What Are Bollinger Bands (BOLL)?
- Historical past and Origin of the Bollinger Bands Indicator
- How Bollinger Bands Work?
- Key Parts of Bollinger Bands
- Tips on how to Interpret Bollinger Bands
- Widespread Buying and selling Methods Utilizing Bollinger Bands
- Bollinger Band Squeeze: Figuring out Breakouts
- Overbought and Oversold Circumstances Defined
- Benefits of Utilizing Bollinger Bands in Crypto Buying and selling
- Limitations and False Alerts
- Combining Bollinger Bands with Different Indicators
- Greatest Timeframes and Belongings for Bollinger Bands
- Sensible Instance: Utilizing BOLL in a Reside Chart (2025 Market)
- Conclusion
- FAQs
In case you’ve ever stared at a chart, watched three strains slide up and down, and questioned what they imply, you’ve in all probability been discussing Bollinger Bands. In buying and selling crypto or shares, when somebody mentions the “BOLL indicator,” it’s one of many first go-to instruments for measuring volatility, recognizing breakouts, or mapping overbought/oversold zones. However realizing what they’re is simply the beginning. To make use of Bollinger Bands as a part of your toolkit, it’s essential to perceive how they had been created, how they work, what they let you know in real-world situations, and the way you mix them with different instruments.
What Are Bollinger Bands (BOLL)?
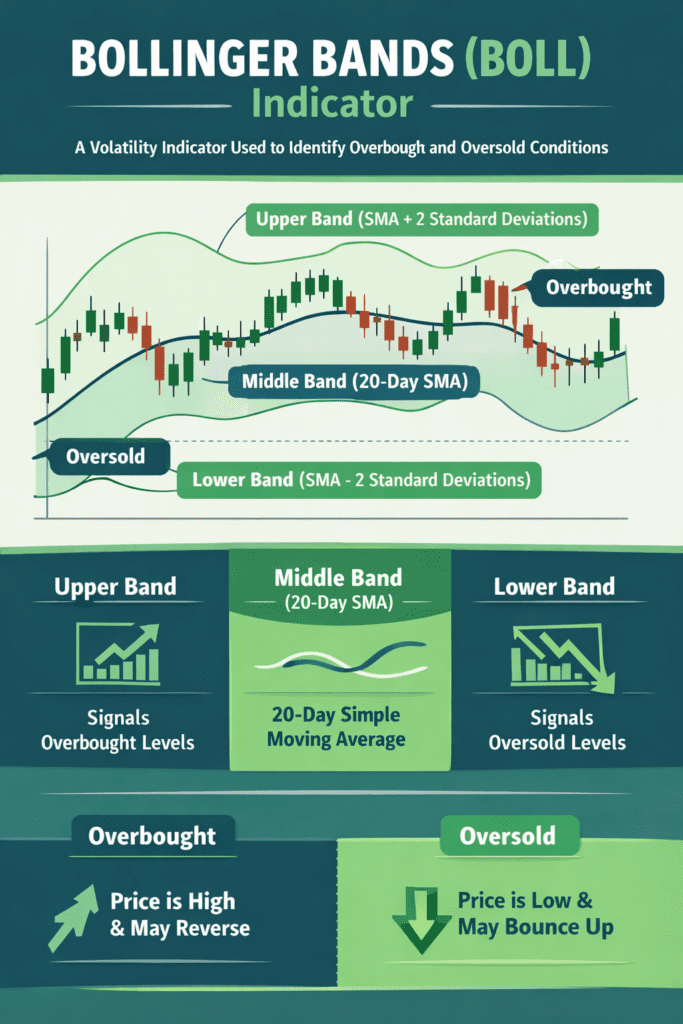
Bollinger Bands are a kind of visible envelope plotted round value knowledge that displays volatility and relative pricing extremes. They include three strains: a center band (usually a 20-period easy transferring common), an higher band (that transferring common plus a a number of of ordinary deviation), and a decrease band (transferring common minus that very same a number of). When the bands widen, you’re seeing an increase in volatility; after they contract, the market is calm, usually ready for its subsequent transfer.
Historical past and Origin of the Bollinger Bands Indicator
The story begins within the early Nineteen Eighties with John Bollinger, a technical analyst who noticed one thing others had been lacking: markets don’t all the time observe a hard and fast volatility sample. Volatility ebbs and flows. Fastened bands round a transferring common usually failed when the market modified tempo. Bollinger got down to construct an envelope system that tailored to volatility. He used normal deviation along with a transferring common to create bands that robotically widen or contract relying on current value variation. He launched these to the general public within the Nineteen Eighties and ultimately trademarked the time period “Bollinger Bands”.
Learn Extra: Relative Strength Index (RSI): Full Form, Strategy Indicator
How Bollinger Bands Work?
On the core of Bollinger Bands is the idea of volatility and mean-reversion (or breakout) potential. The center band tracks the current common value. The higher and decrease bands sit above and under, at a distance outlined by normal deviation. Primarily, when the worth strikes away from the common, it pushes into the outer bands. That tells the dealer: “Hey, value could also be stretched.” If the bands are slender, the market is quiet. Very often precedes a breakout. Extensive bands imply huge strikes have already occurred, and the market could also be fatigued. Utilizing the bands includes watching not simply the place the worth is, however how bands transfer: band contraction indicators buildup; band enlargement indicators execution.
Key Parts of Bollinger Bands
Let’s break down the definitions:
- Center Band (MB): Typically the 20-period easy transferring common (SMA) of the closing value.
- Higher Band (UB): MB + (Okay × normal deviation over N intervals). Default: Okay = 2, N = 20.
- Decrease Band (LB): MB − (Okay × normal deviation over N intervals).
The method could be expressed as:
MB = SMA(value, N)
Higher Band = MB + Okay * σ
Decrease Band = MB − Okay * σ
The place σ is the usual deviation of the worth over the past N intervals.
Tips on how to Interpret Bollinger Bands
Deciphering Bollinger Bands is much less about guessing extremes and extra about studying context. If the worth touches or exceeds the higher band, it could point out overbought situations; touching the decrease band could sign oversold situations. However context issues: in sturdy up-trends, value could hug the higher band for lengthy intervals; in down-trends, value could journey the decrease band.
Learn Extra: Supertrend Indicators: How Do Generate Buy & Sell Signals?
Widespread Buying and selling Methods Utilizing Bollinger Bands
Listed below are a number of methods merchants use Bollinger Bands in crypto markets:
Imply-Reversion Technique: When the market is range-bound and the worth touches the decrease band, take an extended commerce towards the center band or higher band. Conversely, quick close to the higher band towards the center.
Breakout Technique: Throughout a squeeze (very slender bands), count on a directional breakout. Look forward to the worth to interrupt out above the higher band with quantity or under the decrease band with quantity and journey the transfer.
Development-Following with Bands: In trending markets, the worth could journey the higher band (in an uptrend) or the decrease band (in a downtrend). Use the center band as a dynamic cease or exit.
Bollinger Band Squeeze: Figuring out Breakouts
Some of the highly effective setups with Bollinger Bands is the squeeze: when the higher and decrease bands converge tightly, volatility is compressed, and sometimes a giant transfer is ready. Merchants monitor the bandwidth (distance between higher and decrease bands) to determine squeezes. When bandwidth reaches historic lows and value begins to breakout with quantity, that indicators the seemingly begin of a pattern. In crypto markets, the place volatility is excessive and breakout strikes are frequent, the squeeze setup can set off sharp strikes in minutes or hours quite than days.
Overbought and Oversold Circumstances Defined
When value touches the higher band and the market is gradual to interrupt by way of, some merchants see it as an overbought warning. When it touches the decrease band repeatedly with a weak bounce, it could be oversold. However bear in mind: in sturdy directional markets, value can stay on the outer bands for prolonged intervals. Thus, it’s essential to verify value motion indicators (candles, quantity, momentum) in conjunction. An oversold contact on the decrease band could not consequence immediately rebound; it might merely sign continuation of a down transfer.
Benefits of Utilizing Bollinger Bands in Crypto Buying and selling
For crypto merchants, Bollinger Bands deliver clear advantages. First, they adapt: volatility in crypto can spike or collapse inside hours, and the bands broaden/contract accordingly, providing you with a real-time gauge of market temper. Second, they assist standardize ranges: quite than subjective assist/resistance, you could have statistical bands guiding expectations. Third, they work throughout timeframes and property, whether or not you’re buying and selling Bitcoin on a day by day chart or a smaller altcoin on 15-minute frames.
Limitations and False Alerts
No indicator is ideal. The Bollinger Bands indicator additionally has its limitations. They can provide false indicators if used standalone, e.g., value breaks the band and continues in the identical path quite than mean-reverts. Throughout sturdy trending strikes, the bands could also be deceptive: value hugging the higher band isn’t all the time ‘overbought’, it’d simply be momentum. The usage of normal deviation assumes sure statistical distributions, which don’t all the time maintain in crypto markets; fats tails and excessive strikes are widespread.
Combining Bollinger Bands with Different Indicators
To extend reliability, merchants mix Bollinger Bands with different instruments. In style pairs embody: Relative Power Index (RSI), for momentum and overbought/oversold affirmation; Quantity patterns, confirming breakout energy; Transferring Common Convergence Divergence (MACD) or Stochastic Oscillator, for pattern energy or reversal cues. For instance, a squeeze in Bollinger Bands plus RSI under 30 could recommend a robust rebound quickly. Conversely, a value hit on the higher band with RSI above 70 and falling quantity could sign a weakening advance.
Greatest Timeframes and Belongings for Bollinger Bands
In crypto markets, courtesy of 24/7 buying and selling and excessive volatility, Bollinger Bands work fantastically on a number of timeframes, from 5-minute intraday charts to 4-hour and day by day frames. For day merchants or scalpers, utilizing 15-minute or 30-minute charts on high-liquidity cash like BTC, ETH, or SOL offers loads of setups. Swing merchants could use day by day charts with a 20-period SMA and two normal deviation bands.
Sensible Instance: Utilizing BOLL in a Reside Chart (2025 Market)
Think about you’re buying and selling Ethereum (ETH) on a day by day chart in mid-2025. You apply Bollinger Bands with settings 20/2. You discover: the bands have been narrowing for 5 days. Bandwidth hits a brand new low in comparison with final month. That indicators consolidation and low volatility. You set alerts for a breakout above the higher band or a break under the decrease band. The following morning, ETH breaks above the higher band with a quantity spike. You enter lengthy. You set the stop-loss on the center band. As the worth strikes up, the higher band additionally widens. You path cease slightly below the center band. You exit when the worth hits the higher band once more and the quantity lag reveals indicators of exhaustion.
Conclusion
Bollinger Bands stay one of the vital sensible instruments in buying and selling, be it shares or crypto. They provide you a visible framework of volatility, relative value ranges, pattern vs. vary, and breakout chance. However as with all the things in buying and selling, the indicator itself isn’t magic. It really works greatest whenever you perceive its strengths and limitations, and whenever you mix it with different indicators.
FAQs
1. What are Bollinger Bands in buying and selling?
Bollinger Bands are three strains plotted round a transferring common of value: the center band (the transferring common), an higher band above by a a number of of ordinary deviation, and a decrease band under by that very same issue. They adapt to volatility and assist merchants determine relative value extremes.
2. Who created the Bollinger Bands indicator?
The indicator was created by John Bollinger within the early Nineteen Eighties. He developed it to construct volatility-adaptive buying and selling envelopes quite than fixed-width channels.
3. How do Bollinger Bands work?
They work by inserting a transferring common on the heart after which including and subtracting multiples of the usual deviation to create higher and decrease bands.
4. What do the higher, center, and decrease bands symbolize?
The center band represents the straightforward transferring common of value (pattern). The higher band represents a threshold usually two normal deviations above the common (potential overbought or breakout zone).